Now, we will actually read a report to help put all of these into practice.
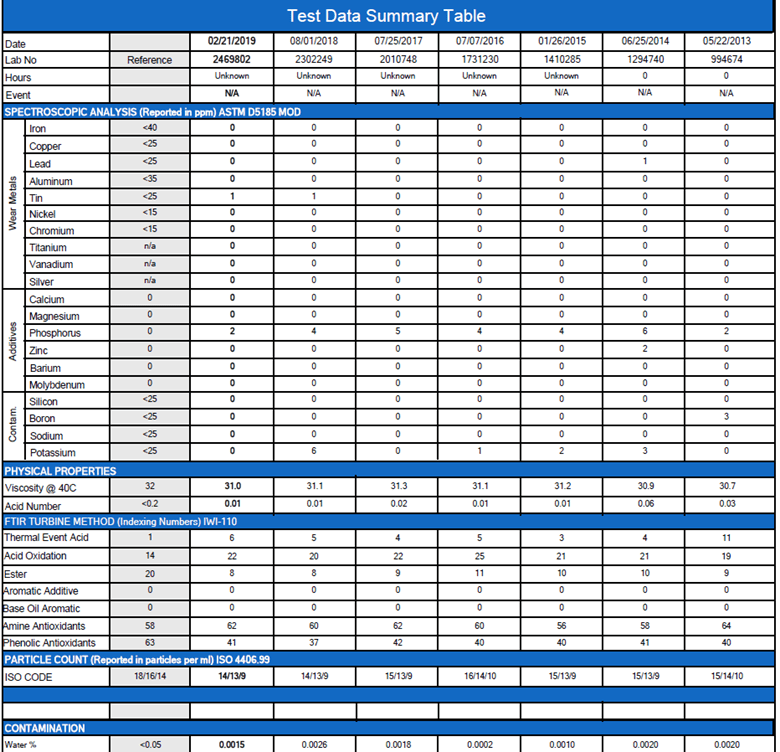
Here is a sample report from Eurofins for a turbine oil. In this report, the various types of tests are classified according to wear metals, additives, and contaminants, as shown in Figure 2.
According to the report, samples have been collected over a period of time. This helps with the trending of the data, so we can spot when the values start varying from the “normal levels”. The reference values are also provided in the first column to help users determine whether these values fall within tolerance limits or not.
Typically, the lab will provide some type of traffic light system where:
- Red – indicates there may be an abnormal reading or the oil should be changed immediately, as certain values have surpassed the critical limits.
- Amber – shows that the values are approaching the warning limits, but there is still some time to investigate and fix the problem.
- Green – tells us that all values are within the tolerance limits and the oil is performing normally.
For this report, they also include additional tests as shown in Figure 3.

For turbine oils, understanding the demulsibility of the oil is important, as this is the oil’s ability to separate from water, or rather, not to form an emulsion. Excessive water in the oil can lead to rust or even a washout of the additives.
The Foam test is also administered to detect the oil’s ability to release air from the oil, ensuring that the air doesn’t get trapped. If air is trapped, it can lead to microdieseling and cavitation on the inside of the equipment.
RPVOT – Rotating Pressure Vessel Oxidation test is also performed, as it indicates the expected oxidation of the oil. MPC (Membrane Patch Colorimetry) and Ultracentrifuge detect the potential of the oil to form varnish, and the RULER® values give the actual quantity of antioxidants present. These values are all critical for monitoring the health of the turbine oil, as it is very susceptible to oxidation and the formation of varnish.
In essence, reading the oil analysis report involves understanding what the tests are meant to measure, knowing your equipment and its operating conditions, and having a history of your equipment. These factors all contribute to trending the data to ensure that there are no surprises with unplanned downtime due to wear or oil degradation.
References
Eurofins. (2025, September 06). Annual Turbine Analysis. Retrieved from Eurofins Testoil: https://testoil.com/services/turbine-oil-analysis/annual-turbine-analysis/
Find out more in the full article, "How to Read Oil Analysis Reports and translate Data into Reliability" featured in Reliable Magazine by Sanya Mathura, CEO & Founder of Strategic Reliability Solutions Ltd.