As the name suggests, antiwear additives help to prevent wear in one way or another. However, what makes them unique compared to other additives in lubricants? Why are they used more predominantly in specific applications than other applications? This article explores antiwear additives, why they are needed, and how they work.
What Are Antiwear Additives?
According to (Bloch, 2009), antiwear agents can also be called mild EP (Extreme Pressure) additives. In some cases, they may also act as antioxidant additives (depending on their chemical structure). In essence, antiwear additives protect against friction and wear when the surfaces experience moderate boundary conditions.
During moderate boundary conditions, the full film of the lubricant has not yet formed, and asperities on both surfaces can come into contact with each other. As such, antiwear additives can also be called boundary lubrication additives.
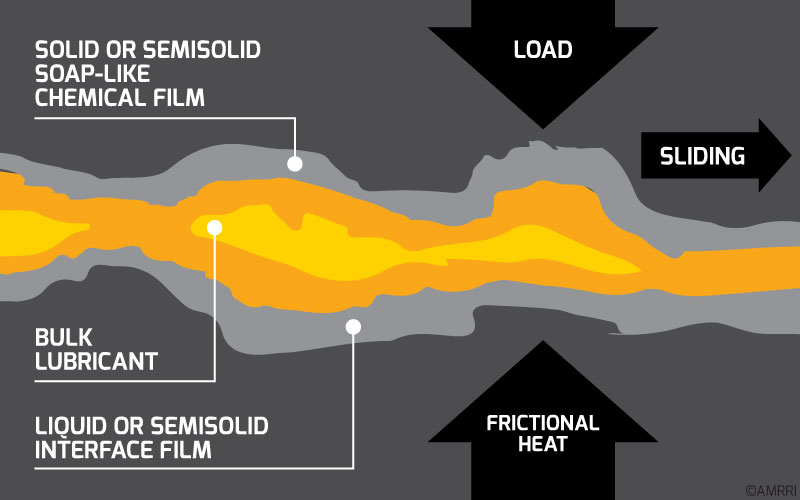
Usually, these antiwear additives react chemically with the metal to form a protective layer. This layer or coating will allow the two surfaces to slide over each other with low friction and minimal metal loss. As such, antiwear additives have also adopted the nickname “anti-scuff” additives.
According to Pirro, Webster, & Daschner, 2016, the adsorbed film on metal surfaces is formed from long-chain materials. In these cases, the polar ends of the molecules attach to the metal while the projecting ends of the molecules remain between the surfaces.
Under mild sliding conditions, wear is reduced; however, under severe conditions, molecules can be rubbed off such that the wear-reducing effect is lost. When this happens, it is evident in the oil analysis data with the presence of wear metals in large quantities.
In essence, antiwear additives help protect the oil while reducing friction, protecting the surfaces, and, in some cases, enhancing the oil to be more resistant to oxidation. While they can perform these functions, it must be noted that there are many different types of antiwear additives.
Want to read the entire article? Find it here in Precision Lubrication Magazine!




