What conditions affect lubricants?
How are your lubricants currently stored?
Are you storing lubricants under the correct conditions?
These questions have come up a dozen times during audits and countless warehouse meetings!
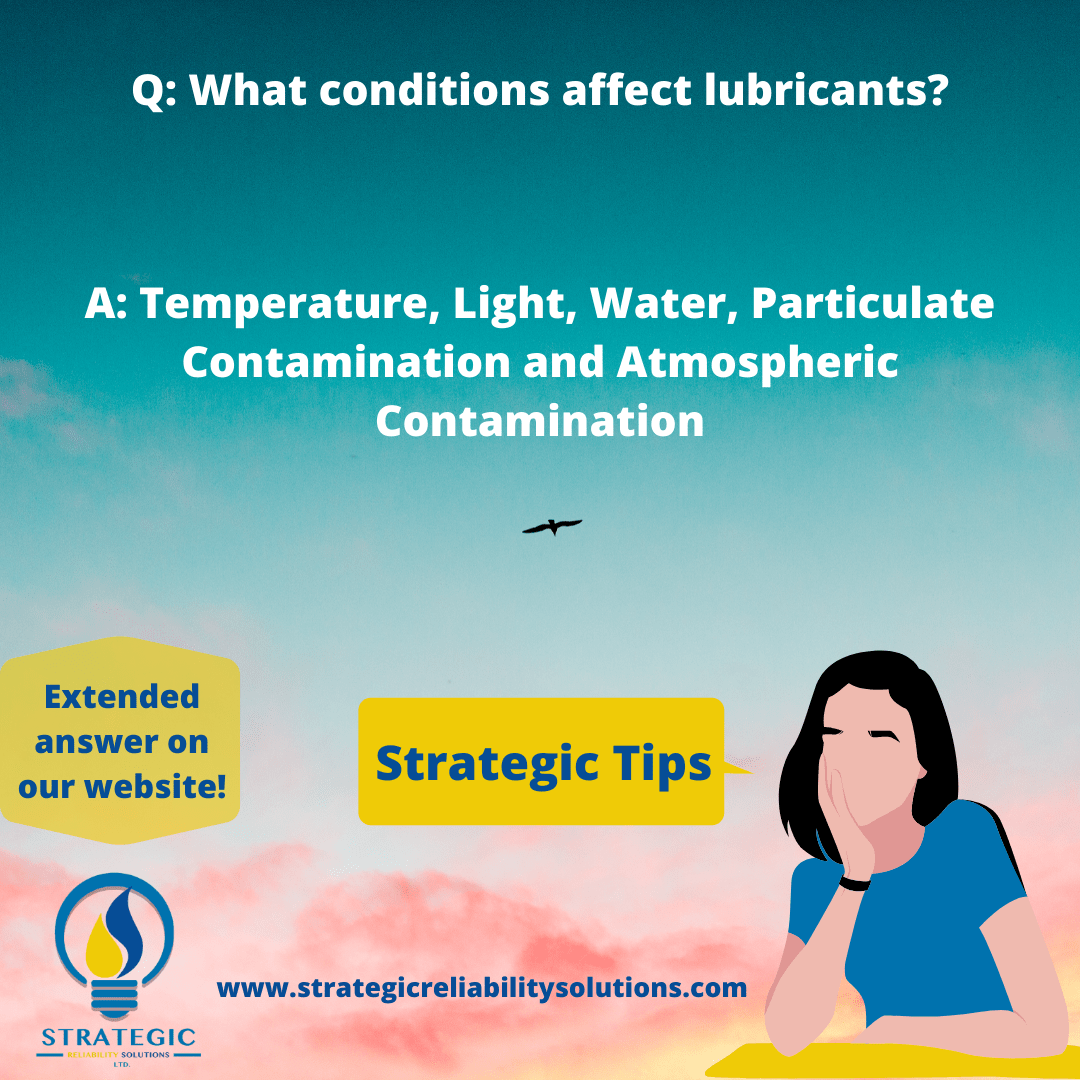

To answer these questions, there are five main conditions that can affect lubricants. We have detailed them along with the effects of these conditions on the lubricant.
- Temperature – if incorrect can lead to oxidation. For every 10C rise in temperature above 40C the life of the lubricant is halved.
- Light – too much can lead to oxidation especially for light sensitive lubricants such as transformer oils. Hence the reason that most packaging is opaque.
- Water – this usually works with additives to cause their depletion or contamination of the product. Water in any lubricant is bad (especially for transformer oils as they are involved in the conduction of electricity.
- Particulate contamination – contamination can occur by air borne particles if packaging is left open or if dirty containers/vessels are used to transfer the lubricant from its packaging to the component.
- Atmospheric contamination – this affects viscosity and promotes oxidation and can occur if packaging is left open. For instance, if a drum is not properly resealed or capped after usage or the most common practice of leaving the drum open with the drum pump on the inside.
Different types of lubricant degradation
Why is it important to know the types of lubricant degradation?
It’s important since it helps us to figure out why or in some instance how, the lubricant degraded! Usually degradation is the change that occurs when the lubricant can no longer execute its five main functions:
- the reduction of friction
- minimization of wear
- distribution of heat
- removal of contaminants and
- improvement of efficiency.


There are 6 main types of Lubricant Degradation as detailed below. Each type produces various by products which can enable us to understand the reason for the degradation and eliminate that / those reasons.
Here are the 6 main types of Lubricant Degradation:
1. Oxidation
2. Thermal Breakdown
3. Microdieseling
4. Additive Depletion
5. Electrostatic Spark Discharge
6. Contamination
As discussed, each mechanism produces distinct results which help us in their identification! Check out our article on why lubricants fail for more info!



